1. 机器学习简介和Python的基本操作
本文最后更新于 2025年9月1日 上午
机器学习简介和Python的基本操作
Before the course…
- Software and environment: Anaconda and Opencv
- Ultimate Project: Traffic Sign Recognition
- There’s a individual Quiz on lecture 5
人工智能的产生
lines of codes programming forces people to find a way to teach the program to do things. example: makeup transfer example: auto ping-pong machine
计算机视觉简介
计算机视觉可以大致的被分为三个大类:
- 3D建模(3D Construction)
例子:敦煌莫高窟的3D建模(来自武汉大学)
- 图像渲染(Image Rendering)
例子:Google Pixel
其搭载的增强现实算法能够对周围的图像进行实时渲染
- 图像检测(Pattern Recongnition)
例子:都灵的图像识别装置
人们穿戴对应的设备行走,设备能够识别他周围的物品
计算机视觉可以在各个领域帮助到人们,在医学领域帮助医生识别X光片,在自动驾驶领域,自动驾驶汽车依靠车身上的传感器和相机识别道路上的物体,在体育竞技领域,计算机视觉能够帮助人们更好的训练运动员的运动姿势。世界上第一张人脸检测的图片由Dr.Sung Kah Kay在1996年完成。
计算机科学的知识架构:

Python 的基本操作
简介
Python 不需要编译,是机器学习的首选语言之一,有非常多的库能够被调用。 Python支持超大的数字运算
编译环境(IDE):Anaconda, 适用于大数据环境
> 不要使用 Python 2.x
- Python的IDE思路:REPL
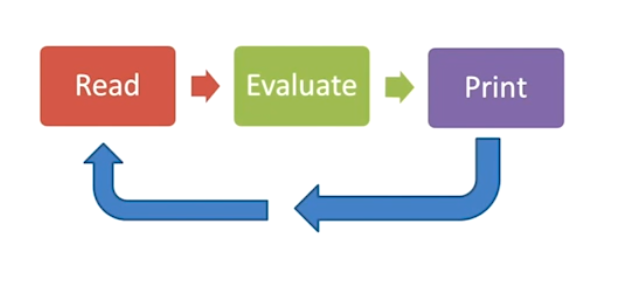 Reading: 读取来自键盘等的输入
Reading: 读取来自键盘等的输入
Evalueate: 将输入进行Evaluate,其结果通常是一个数值,这个数值最终会被编译器输出(Print)
在输出后,这个程序将等待下一次的输入,形成一个循环
赋值和函数定义
Python可以不用声明变量的类型,直接对其进行赋值,其变量的赋值类型取决于赋值
Python支持同时对多个变量进行赋值:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8a,b=c,d
```
定义函数的结构:
``` Python
def functionname(variable):
return value
# 也可以不需要返回值
1
2
3
4
5 function= lambda return_variable: options
```
例如:
``` Python
S= lambda x: x*x
- 嵌套调用:
funcationname(funcationname(variable))
- 在Python中,变量可以传递给函数,函数也可以传递给变量。
例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7def function (n):
n*n
return n
foo=function(5)
# 此时foo的类型是一个函数
foo(10)
# >> 100 - 可以在定义函数的部分嵌套定义其他函数:
1
2
3
4def function(variable1):
def subfuntion(variable2):
return variable2
return variable1
条件结构(if-else)
条件语句的基本结构: 1
2if conditon:
options1
2
3
4
5
6def compare(a,b):
if a>b:
return a
return b
compare(3,4)
#>> 41
2
3
4
5
6
7
8if condition1:
options
else if condition2:
options
else if condtion3:
options
else:
options
循环结构
通过函数定义的返回值来进行循环 (recursion) 例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7def factorial(n):
if n==1:
return 1
return n*factorial(n-1)
factorial(5)
#>> 120
#5*4*3*2*1通过for循环语句来进行循环(for-range)
例如:1
2for innnervariable in list #usually is range(a,b) a to b do n++
options
> 要注意1
2
3
4
5
6def factorial(n):
for x in range(1,n+1)
result=result*n
return result
factorial(5)
#>> 120range(a,b)是不包括b的:
>>这样的循环结构没有自增加(1
2
3for a in range (0,4)
print(a)
#>> 3x++)的存在通过while语句进行循环
例如:1
2while (condition):
options1
2
3
4
5def gcd(a,b): #最大公约数
while (b>0):
r=a&b
a,b=b,r
return a
字符串
在Pyhton中,字符串由双引号”“或者单引号’’定义。 字符串支持加减法: 1
2'hello'+'world'
#>> 'helloworld'1
2'hello'*3
#>> 'hellohellohello'
- 字符串的传递
字符串可以传值给变量(类型是字符串),可以通过[起点:终点:步长]访问字符串中的特定位置的字符。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11a='helloworld'
print(a[2])
#>>'l'
print(a[0:4])
#>>'hello'
> Python 中的序号是从0开始的
print(a[::-1] )
#>>'dlrowolleh'
b='abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
print(a[1:15:2])
#>>'bdfhjln'len()函数将返回字符串的长度[]默认的访问顺序是从左到右,负号(-)表示从右到左的访问顺序。1
2len(hello)
#>> 5
列表
列表(list)是一种参数类型,例如: 1
2
3x=[1,2,3,4]
type(x)
#>> list
列表中的元素可以是任何类型。
和字符串一样,可以用[]来访问列表中特定的某一个或者多个元素。
- 列表的操作
- append()
append()函数将在列表最后一位加上()内的字符串后,输出整个字符串1
2
3
4x=[1,2,3,4]
x.append(2)
print(x)
#>>[1,2,3,4,2] - 列表理解(list comprehension)
在列表的[]中填入生成列表的方法: 例如:可以利用列表理解来过滤某些元素:1
2
3
4
5
6x=[a for a in range(1,8)]
print x
#>> [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
y=[square(a) for a in x]
print y
#>>[1,4,9,16,25,36,49]1
2
3
4
5
6def iseven(n):
return n%2==0
x=[a for a in range(1,8)]
y=[square(a) for a in x if iseven(a)]
print y
#>>[4,16,36]